Reference Books: 1)Behrouz A. Forouzan 2)Data Communications and Networks. by author: ACHYUT GODBOLE 3) Computer Networks by ANDREW S. TANENBAUM
Thursday, 30 August 2012
Wednesday, 29 August 2012
Monday, 27 August 2012
Wednesday, 22 August 2012
Saturday, 18 August 2012
Friday, 17 August 2012
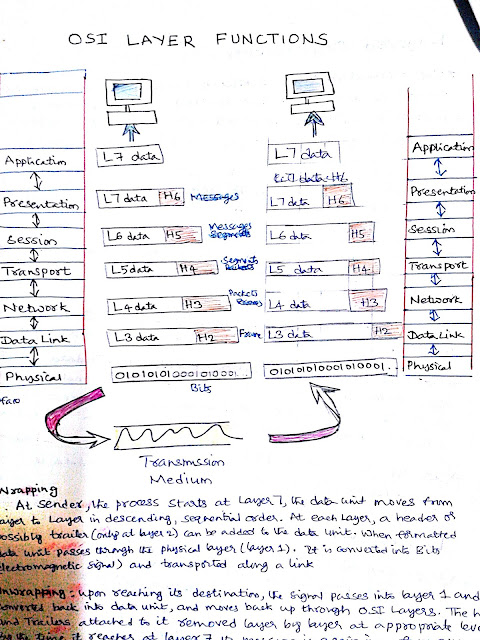
OSI Reference Model
Application Layer
• ‘Closest’ layer to the user
• Works with the applications you use to communicate over the network
E.g.. Services include SMTP, HTTP and FTP
• Clicking on a link on a web page issues a command for the browser to retrieve the relevant information from the Internet
• As an example say your computer is the source,
and the host of the web site information is the
destination
• The application completes your request and
delivers the information to your computer
This layer has three fundamental functions
(1) Data presentation
(2) Data compression
(3) Data encryption
Data Presentation
• Enables receiving device to understand the information sent from the source
• Converts data from native format (abstract syntax) to a common format (transfer syntax), e.g. ASCII
Data Compression
• By reducing the volume of data, transfers can take place in less time
• Packets are examined and such things as spaces in text removed
• The destination device returns the data to its original format before passing to the Application Layer
Data Encryption
• Allows data to be converted to a form which hides its meaning, apart from those you wish to see it
• Not all data is encrypted on its journey across the network
• In order for decryption to occur at the destination device a ‘key’ is required
• Primarily responsible for handling the session between devices (beginning, maintaining and finishing)
• Enforces order in the communication between devices
• Regulates the flow of data
• It takes responsibility for the following
Session services
The following services are provided by Session Layer
• Establishing a connection
• Maintaining the session
• Ending the connection
• Dialogue control
• Dialogue separation
• Handshaking – SYN and ACK packets
• ‘Keep alive messages’
• Session must be terminated (otherwise one device will be still transmitting without any device actually listening)
• Dialogue control (simplex, half-duplex, full-duplex)
• Dialogue separation – checkpoints within the
• transmission which allow the detection of lost packets,
• and subsequent re-transmission
Application Services
• File services
• Electronic-mail services
• Network-printing services
• Application services
• Database services
Functions of Transport Layer
• Ensures reliable transport of packets from source to destination
• It performs multiplexing, segmentation at sending end
• It performs de-multiplexing and reassembly at the receiving end
• Manages the speed of transmission – flow control
• There are two types of transmission
- Connection-oriented transmissions
- Connectionless transmissions
Connection-Oriented Transmissions
• Also known as ‘ Reliable Transport Method’
– uses acknowledgement (ack) packets on
successful receipt of data
• Extra packets slows down communication
Features are
• Reliability
• Slower communication
• Packets are re-transmitted if corrupted or not
received
• Once all the data is received successfully, the
packet is re-assembled and passed to the Session
Layer
Connectionless Transmissions
• In this mode, the transmitting device does not require
acknowledgements from the receiver, and continues
to transmit on the assumption that the data was
received
• Features are
– Little or no reliability
– Faster transmission
– Packets are not re-transmitted
Flow Control
• Establishes the maximum speed at which both sender and receiver can communicate at
• Transport Layer determines largest packet size which can be sent
• Packets are numbered – to allow re-assembly in the correct order
Network Layer
• Network layer packets are known as datagrams
• Uses the network address ( this is a logical address – and does not depend upon any hardware in the device, or the device’s physical location)
Functions of Network Layer
The Network Layer performs the following functions
• Adds the address to the packet (encapsulation)
• Responsible for the correct addressing and delivery of packets of data
• Maps the network address to the device physical address
• Determines the best path for the packet (routing)
• Divides outgoing messages into datagrams and assembles incoming datagrams into messages for higher layer
• Ensures that the packet is in the correct format for the destination
How does it Work ?
• If a packet must move to another network, a routing
protocol is required
• If different packet lengths are used on the different
networks, the Network Layer formats the data accordingly
• The primary piece of hardware which works on this layer is
the router. (covered in detail, later in course)
Data Link Layer
• Has two sub layers of its own
– Logical Link Control (LLC)
– Media Access Control (MAC)
– LLC acts between protocols such as Internet Protocol (IP) and the MAC method
• MAC is responsible for the connection to the physical media (e.g. cable)
Medium Access Control (MAC)
• Each NIC has a unique number hard coded into the card called its physical address
• The first 6 digits denote the manufacturer, the next six are unique) – type “winipcfg” on your PC to get physical address
• When the MAC address is added to the packet it is now known as a frame
• It now has all the information required to travel from the source to the destination
Functions of Data Link Layer
• Synchronization of data frames
• To take the packets from the upper layer (i.e., network layer) converts them into frames
• To take bits from the lower layer (i.e., physical layer) converts them into packets
• Error detection and control
• Framing
• Ensures link level reliability
Quiz
3. Data Link layer deals data in terms of
(a) packets (b) Frames (c) Messages (d) Stream of bits
4. How many sub layers does a Data Link layer
consist of
(a) 3 (b) 2 (c) 4 (d) 5
• To activate, maintain and deactivate the physical connection
• To define voltages and data rates needed for transmission
• To convert the digital bits into electrical signal and vice versa
• To decide whether the transmission is simplex, half duplex or full duplex
• To take the data from upper layer (data link layer) and sends it in the form of digital pulses through the media
To take digital pulses from cable and convert them into bits and send them to data link layer
Physical layer
Quiz
1. The top most layer in OSI model is _____________
(a) Transport (b) Network layer (c) Application (d) Session
2. Data encryption will be done at
a) Session (B) Data link (c)Presentation (d)Transport
3. Dialogue control will be done at ____________________
(a) Presentation (b) Session (c) Transport (d) Physical
4. SMTP, FTP services are provided by ______________
(a) Application layer (b) Presentation layer (c) Session layer (d) Transport layer
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)

































.JPG)
.JPG)
osi.JPG)
.JPG)
.JPG)
.JPG)
.JPG)




.jpg)

